Attribution models play a very important role in digital marketing. Every business wants to know which marketing channel brings sales, leads, or conversions. Customers usually interact with many ads, websites, emails, and social media posts before they buy. Attribution models help businesses understand which touchpoints deserve credit for the final conversion.
In simple words, attribution models explain where conversions come from. They show how customers move through the buying journey and which channels influence their decision. Without attribution models, businesses may spend money on the wrong channels and lose growth opportunities.
This article explains attribution models in easy English. It covers types of attribution models, examples, benefits, common mistakes, and best practices.
What Are Attribution Models
Attribution models are rules used in digital marketing to assign credit to different marketing channels or touchpoints that lead to a conversion. A conversion can be a sale, lead, sign-up, or any important action.
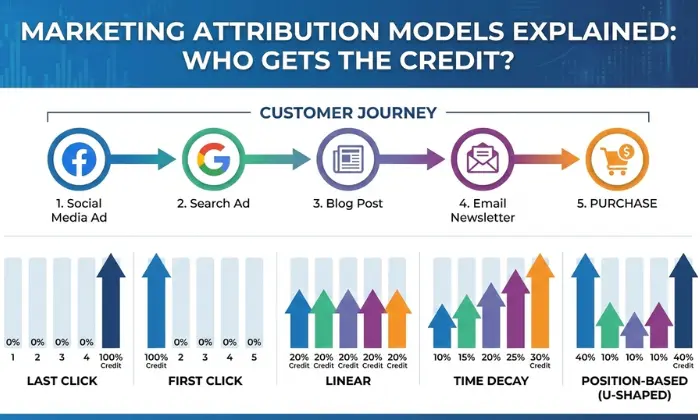
For example, a customer may:
- See a Facebook ad
- Click a Google search ad
- Read a blog post
- Receive an email
- Finally make a purchase
Attribution models decide how much credit each step gets for the conversion.
Why Attribution Models Are Important
Attribution models help businesses make better marketing decisions. They show what really works and what does not.
Main benefits include:
- Better budget allocation
- Improved ROI
- Clear understanding of customer journey
- Better marketing strategy planning
- Improved campaign performance
Without attribution, marketers may stop campaigns that actually help conversions.
How Attribution Models Work
Attribution models track customer interactions across channels using cookies, tracking codes, and analytics tools. When a conversion happens, the model assigns credit based on predefined rules.
Different models assign credit differently. Some give full credit to one channel, while others share credit among multiple channels.
Single-Touch Attribution Models
Single-touch attribution models give 100% credit to one interaction in the customer journey.
Last Click Attribution
Last click attribution gives full credit to the last interaction before conversion. This model is simple and widely used.
Example:
If a customer clicks a Google ad and then buys, Google ad gets full credit.
Advantages:
- Easy to understand
- Simple to track
Disadvantages:
- Ignores earlier touchpoints
- Does not show full customer journey
First Click Attribution
First click attribution gives full credit to the first interaction.
Example:
If a customer first visits your site from a Facebook ad and later converts, Facebook gets full credit.
Advantages:
- Shows how customers discover your brand
- Useful for awareness campaigns
Disadvantages:
- Ignores conversion-driving channels
Last Non-Direct Click Attribution
This model ignores direct visits and gives credit to the last non-direct channel.
Example:
If a user comes via Google ad, later visits directly, and converts, Google ad gets credit.
This model is commonly used in analytics tools.
Multi-Touch Attribution Models
Multi-touch attribution models share credit across multiple interactions.
Linear Attribution
Linear attribution gives equal credit to all touchpoints.
Example:
If four channels are involved, each gets 25% credit.
Advantages:
- Fair distribution
- Shows full journey
Disadvantages:
- Treats all touchpoints equally even if some are more important
Time Decay Attribution
Time decay attribution gives more credit to touchpoints closer to conversion.
Example:
Recent interactions get higher credit than early ones.
Advantages:
- Focuses on conversion-driving steps
Disadvantages:
- Undervalues early awareness channels
Position-Based Attribution
Position-based attribution gives more credit to first and last interactions.
Common distribution:
- 40% to first click
- 40% to last click
- 20% shared among middle interactions
Advantages:
- Balances awareness and conversion
- Shows key touchpoints
Disadvantages:
- Fixed rule may not suit all businesses
Data-Driven Attribution
Data-driven attribution uses machine learning to assign credit based on real data.
It analyzes:
- Conversion patterns
- User behavior
- Historical performance
Advantages:
- More accurate
- Customized credit distribution
Disadvantages:
- Requires large data volume
- More complex
Attribution Models in Google Analytics
Google Analytics offers multiple attribution models. Marketers can compare models to understand differences.
Commonly available models include:
- Last click
- First click
- Linear
- Time decay
- Position-based
- Data-driven
Comparing models helps in better decision-making.
Choosing the Right Attribution Model
There is no single best attribution model. The right model depends on your business goals.
Consider:
- Sales cycle length
- Number of touchpoints
- Marketing channels used
- Business objectives
Short sales cycle may work with last click. Long sales cycle benefits from multi-touch models.
Common Attribution Mistakes
Many businesses make mistakes with attribution.
Common mistakes include:
- Relying on only one model
- Ignoring multi-touch journeys
- Not tracking all channels
- Overvaluing last click
- Not reviewing data regularly
Avoiding these mistakes improves marketing performance.
Best Practices for Attribution Modeling
To get the best results:
- Track all marketing channels
- Use multi-touch models
- Compare different models
- Align attribution with goals
- Review data regularly
- Combine attribution with business insights
Attribution is a guide, not a rulebook.
How Attribution Models Improve ROI
Attribution models help businesses spend money wisely. They identify high-performing channels and remove wasteful spend. This leads to better ROI and faster growth.
Future of Attribution Models
With privacy changes and cookie restrictions, attribution is evolving. Businesses now focus on:
- First-party data
- Consent-based tracking
- Modeled conversions
- Server-side tracking
Modern attribution focuses on privacy and accuracy.
FAQ
What is an attribution model in simple words?
An attribution model shows which marketing channels help bring conversions.
Which attribution model is best?
There is no single best model. It depends on your business and goals.
Is last click attribution outdated?
It is simple but limited. Multi-touch models give better insights.
Can small businesses use attribution models?
Yes. Even basic attribution helps improve marketing decisions.
Does attribution help improve ROI?
Yes. It helps allocate budget to the right channels.
Conclusion
Attribution models are essential for understanding marketing performance. They help businesses see the full customer journey and make smarter decisions. By choosing the right attribution model and reviewing data regularly, marketers can improve ROI, reduce waste, and grow effectively.
Attribution is not about perfection. It is about better understanding and better decisions.